Anatomy of the Body
The Powerhouse Glutes: Unveiling the Three Muscles That Steer Our Stability

As Pilates instructors, understanding the anatomy that underpins our clients’ movements can empower our teaching techniques. Among the most influential muscles are the glutes. This trio – Gluteus Maximus, Gluteus Medius, and Gluteus Minimus – not only bestow our body with strength, but also play a pivotal role in stabilising the pelvis. Dive with us into the intricate world of these powerhouse muscles and learn how to harness their strength.
1. GLUTEUS MAXIMUS: THE MAJOR PLAYER
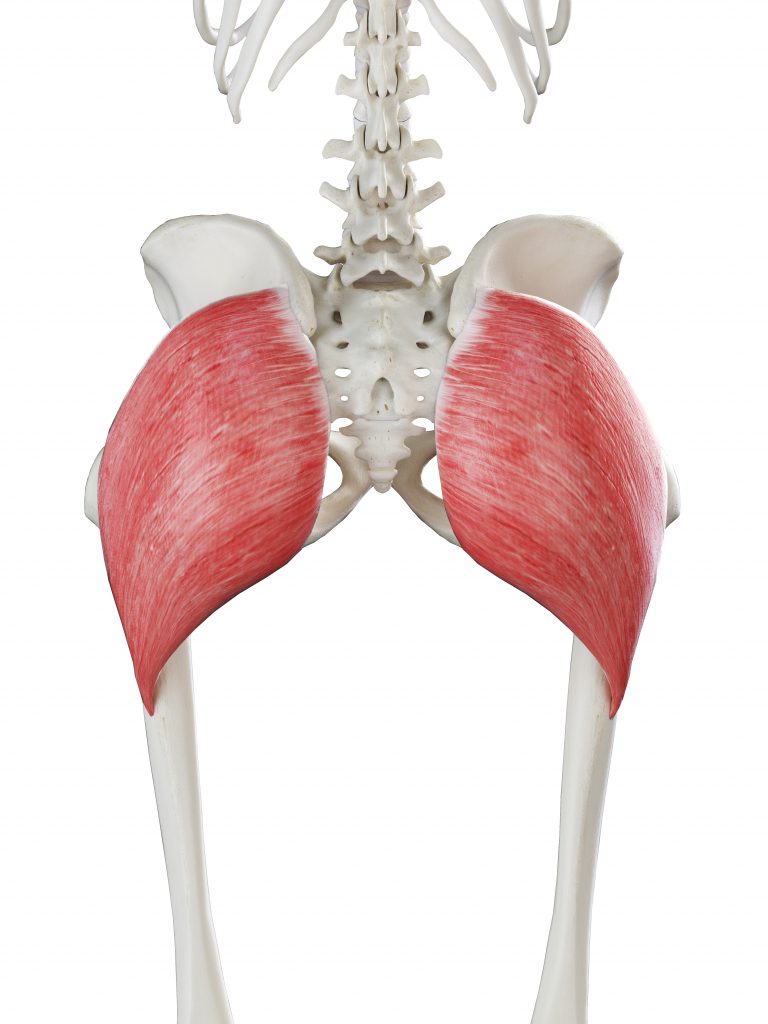
Largest among the trio, the Gluteus Maximus is the outermost muscle.
Function: Responsible for hip extension, outward rotation, and abduction of the thigh. The Gluteus Maximus is crucial during activities like climbing stairs, running, and standing up from a sitting position.
2. GLUTEUS MEDIUS: THE STABILISER
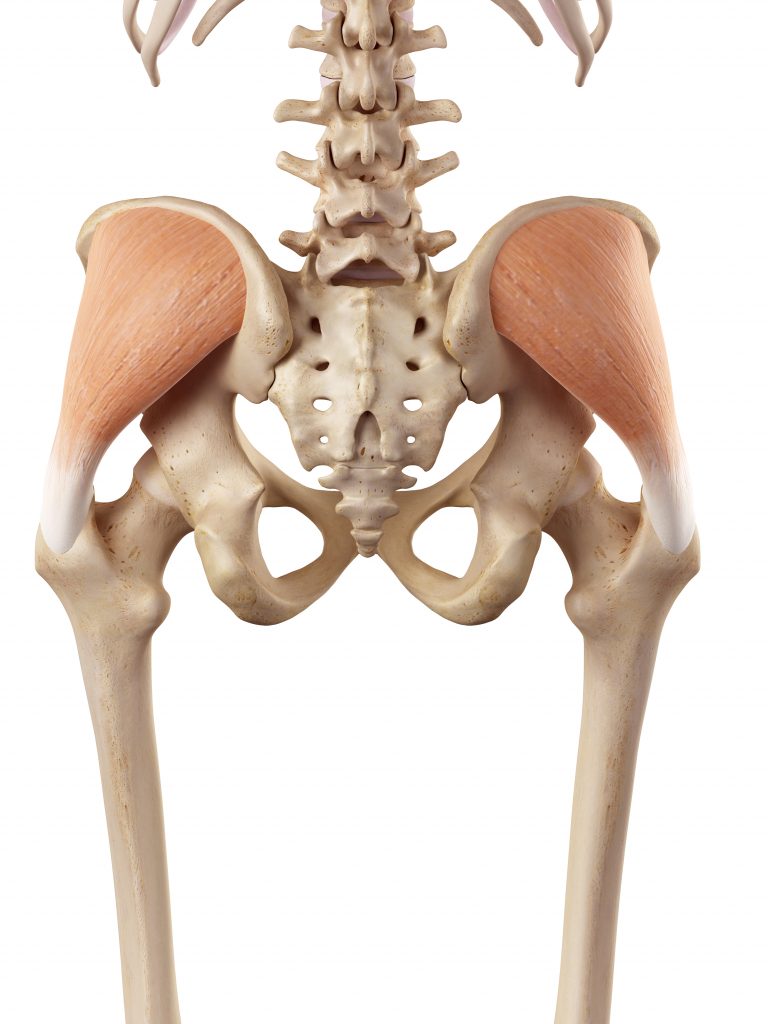
Situated slightly above and to the side of the Gluteus Maximus, its crescent shape has a pivotal role.
Function: A primary muscle for hip abduction. It prevents the pelvis from dropping to the opposite side while walking, maintaining a balanced stride.
3. GLUTEUS MINIMUS: THE SUPPORT SYSTEM
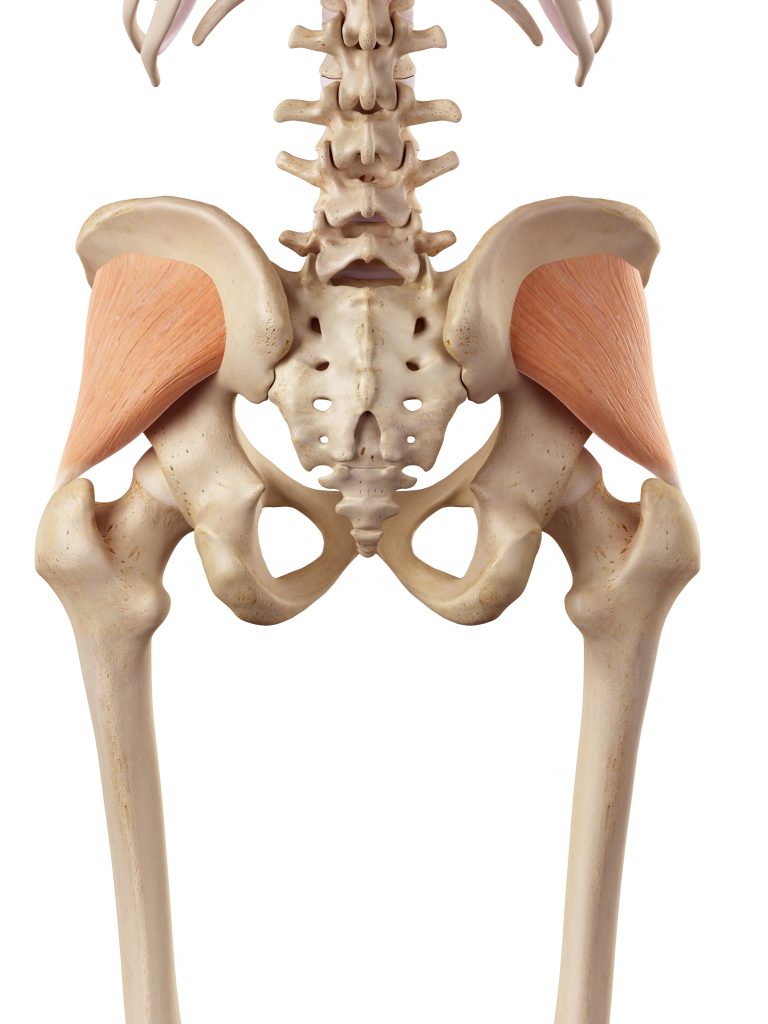
Located beneath the Gluteus Medius, it’s the smallest glute muscle.
Function: The Gluteus Minimus assists in hip abduction and internally rotates the thigh. Working in harmony with the Medius, it aids in pelvic stability.
REASEARCH ON THE SIGNIFICANCE OF ROBUST GLUTES
The strength of the gluteal muscles isn’t just about aesthetics; it’s integral to injury prevention and overall body health.
Injury Prevention
Weak or imbalanced glutes can contribute to various injuries, from runner’s knee to shin splints and even lower back pain. It is common for athletes, especially runners, to have a weaker Gluteus Medius, which may result in lateral hip pain (Semciw et al., 2013).
Stability and Balance
The glutes play a cardinal role in pelvic and spinal stability. Further, the glutes contribute to balance, ensuring our body remains upright during standing and dynamic activities.
Posture and Movement
Beyond injury prevention, glutes are integral for movement efficiency and posture. Distefano et al. (2009) emphasised that strong glutes are vital for functional movements, from squatting to lunging and jumping.
PILATES AND THE GLUTEALS
Harnessing the power of the glutes is integral in Pilates. With a focus on core strength and pelvic stability, Pilates exercises engage and strengthen these muscles, offering clients a comprehensive workout that encourages functionality and injury prevention.
The glutes, with their distinct roles and collaborative functioning, are foundational to our movements and stability. As Pilates instructors, an in-depth understanding of these muscles and their relevance can shape our teaching and also offer clients insight into their bodies.
REFERENCES
Distefano, L. J., Blackburn, J. T., Marshall, S. W., & Padua, D. A. (2009). Gluteal muscle activation during common therapeutic exercises. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, 39(7), 532-540.
Semciw, A. I., Neate, R., & Pizzari, T. (2013). Running related gluteus medius function in health and injury: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology, 23(5), 1240-1248.